Introduction
The pharmaceutical drug serialization regulations in Jordan are formulated and overseen by the Jordan Food and Drug Administration (JFDA). These regulatory measures were established to ensure the integration of serialization and traceability systems within the pharmaceutical supply chain. Aligning with international standards and best practices, these regulations are crucial for the industry.
The serialization systems adopted by the JFDA are designed to be interoperable with global systems, enhancing the seamless movement of pharmaceutical products across borders.
Key Regulatory Areas per JFDA:
Regulations: The JFDA has instituted regulatory requirements for pharmaceutical serialization that adhere to global standards, including guidelines from entities such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
Serialization Standards: Pharmaceutical manufacturers and distributors in Jordan must comply with specific serialization standards, like the GS1 global standards, to ensure the unique identification of each product.
Data Management: The serialization process involves capturing and managing data related to each serialized product, encompassing product information, batch numbers, expiration dates, and unique serial numbers, typically stored in a centralized repository or database.
Traceability: This system facilitates tracking and tracing pharmaceutical products at various points along the supply chain, from manufacturing to distribution and dispensing.
Verification: Stakeholders within the pharmaceutical supply chain, such as pharmacists and wholesalers, can verify the authenticity and legitimacy of products through serialized codes.
Note of Caution from JFDA:
Pharmaceutical companies operating in Jordan must comply with serialization regulations. Non-compliance could lead to regulatory actions and penalties.
Timelines:
Established in 2003, the JFDA ensures drug safety and efficacy, and food quality and safety. The implementation of 1D linear and 2D data matrix codes had been postponed several times in recent years, but the JFDA has now set new regulations for the application of 2D data matrix codes and serialization on secondary packaging of pharmaceutical products. The last update from JFDA was that all pharmaceutical products must have a DataMatrix and be serialized by September 30, 2023.
Product Identification:
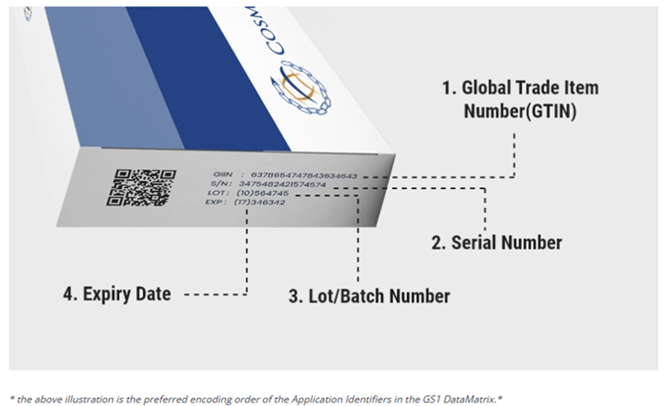
To facilitate accurate reading, a two-dimensional bar code with Human-Readable Information (HRI) should include:
- GTIN: A maximum 14-digit code for unique global product identification.
- Batch number: Up to 20 alphanumeric characters.
- Expiration date: Represented as YYMMDD.
- Unique Serial number: Variable length up to 20 alphanumeric characters.
Compliance:
Pharmaceutical companies should collaborate with supply chain partners and technology vendors to ensure their serialization solutions align with JFDA regulations and meet deadlines. Non-compliance could lead to penalties and delays in product registration and market access in Jordan.
How Can CosmoTrace Help?
CosmoTrace offers serialization consulting, implementation, and integration services to assist clients in managing end-to-end serialization projects and preparing for global regulations. Proficient in compliance regulations for various markets, we specialize in implementing Jordan's pharmaceutical serialization requirements. Our team strategizes solutions leveraging extensive knowledge in product serialization, pharmaceutical supply chains, life sciences, and brand integrity.
Disclaimer:
This information is provided 'As Is' and does not claim suitability for a specific purpose. It represents one interpretation of public domain information and may change. It is not legal advice; users must refer to the source material for complete requirements and form their own interpretation before making business decisions. Please take a look at the source references for updates.
References


