In today’s world of Pharmaceutical Serialization where we have dozens of different regulations and laws pertaining to pharmaceutical and medical device serialization across the globe, the Quality Person (QP), Quality Assurance (QA) or Quality Control (QC) team in the pharmaceutical industry has to put in a lot of efforts to validate the entire system and ensure that all the process, procedure and method is working correctly and would consistently lead to the expected results.
Looking at the level of quality standards in the pharmaceutical industry, the QA/QP/QC expert role is extremely important across the whole process to minimize the risks and ensure proper alignment for the selection, implementation and maintenance of quality system with the authorities’ requirements.
Key factors to consider while validating the system
The entire process of system validation is considered to be one of the most complicated steps in the pharmaceutical industry and there are 3 key factors which are mostly affected:
1. Schedule – System implementation requires installation and qualification of a data center, backup and restore processes, server installations and establishing connections with various interfaces followed by testing and creation of documented evidence to assure proper functioning of the system which takes a long time to complete.
2. Budget – System validation can be an expensive and recurring process if the system governance procedures have not been correctly established or the team is not experienced. To minimize the validation expenses, the risk-based approaches should be used or partnering with your vendors can be another way to keep the validation costs in check.
3. Resources – Validation can be a large burden on internal resources if the responsibility is not properly shared or managed within the teams or with external consultants/partners.
Following the industry standard is a must
System validation is an ongoing process which requires system governance to determine how the system will be regulated, monitored and managed. In addition, proper procedures need to be in place for system administration, change control, new system or functionality releases and other items related to the system to ensure that the validation is maintained. The validation should be performed according to the pharmaceutical industry’s regulation such as GAMP 5, FDA’S 21 CFR PART 11, EU GMP ANNEX 11.
Most pharmaceutical companies follow the GAMP®5 V-Model (Good Automated Manufacturing Practice V-Model) to validate their system as it meets the requirements of the industry regulators. This model is used to define the relationship between requirements and specifications and the verification and testing performed on them.
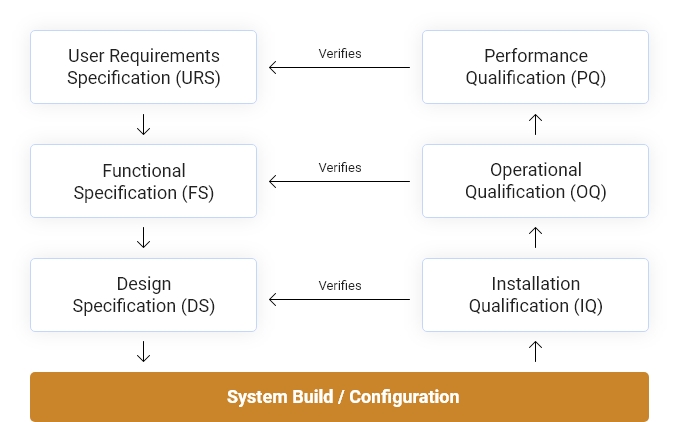
Necessary validation documents must be in place
To reduce the effort of a QA, QP, QC, one can ask their system vendor/partner to provide them with a detailed set of quality documents as per the current industry standards such as GAMP 5 guidelines, GxP and FDA regulations/recommendations. The vendor offering the validation services must go through the unique requirements and processes of the company and include the following deliverables:
- Validation Master & Site Plans
- Test cases separately for each regulation
- IQ, OQ & PQ validation report
- Validation summary report
- Risk Analysis & Mitigation Plan
- Traceability Matrix
- Production Approval Plan
- Impact assessment analysis reports for any new updates/versions
Apart from these, the vendor should also offer the services to review the internal & external documents of the organization, like the SOPs, training records, change management, quality plan, internal risk assessment, vendor functional and design specifications, documents for FAT (Factory Acceptance Test) & SAT (Site Acceptance Test) etc and perform gap analysis to analyze the missing documents and create them wherever required.
It is also important to constantly update the documents, monitor and re-validate the system when the corresponding system changes or when a new feature is released that impacts your unique processes. With upcoming and changing regulations and requirements, new releases of a Level 4 system are a very common thing. However, what is critical is with every new release that you perform a risk-based impact assessment to determine how this change will impact your internal process and whether any validation is necessary. These processes will ensure that your software is in the validated state and especially if it is on multi-tenant architecture.
How can CosmoTrace help?
We provide validation consulting, implementation & integration services to help our clients with managing the end-to-end validation activities and risk management. Our Validation Package consists of various levels of tests, checklists, and reports, and can be tailored to your needs to ensure no information gaps arise.
Our team of experts strategize and plan end-to-end solutions using a combination of years of knowledge in Product Serialization, Pharmaceutical Supply Chains, Life Sciences and Brand Integrity.
To learn more about CosmoTrace visit www.cosmotrace.com. Follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter for Serialization and industry related updates.
Need a helping hand in ensuring smooth operations in your serialization efforts.


